The software that enables a global corporation to measure its carbon footprint and report on its social impact is a sophisticated, data-intensive system that has become the "ERP for non-financial data." A modern ESG Reporting Software Market Platform is architected as a comprehensive, cloud-based ecosystem designed to automate the entire ESG data lifecycle. The architectural foundation of this platform is the Data Ingestion and Integration Layer. This is the critical "front door" for the vast and diverse streams of ESG data, which are often scattered across an organization in a multitude of different systems and formats. This layer is designed with a rich library of connectors to automatically pull in data from a wide range of sources. This includes direct API integrations with utility providers for electricity and water data, connections to internal enterprise systems like ERPs (for procurement and supply chain data), HR systems (for employee diversity and safety data), and even IoT sensor platforms for real-time energy monitoring. It also includes powerful tools, like configurable online surveys and questionnaires, for collecting qualitative and quantitative data directly from suppliers, facility managers, and other stakeholders across the globe. This automated data collection is the crucial first step that eliminates the immense manual effort of chasing down data from hundreds of spreadsheets.
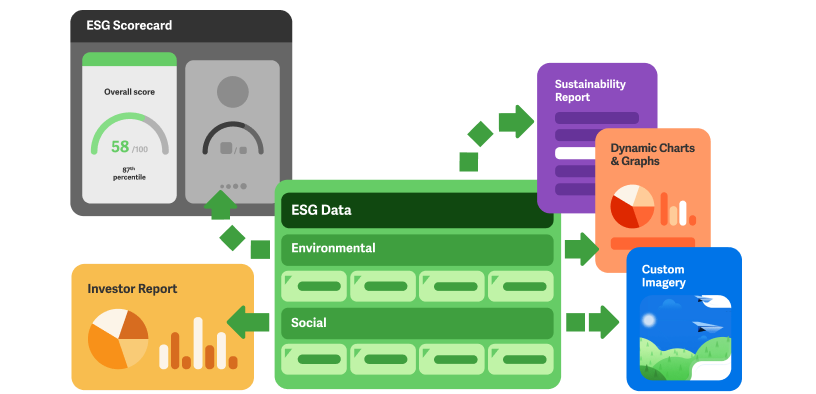
Once the raw data is collected, it flows into the Calculation Engine and Centralized Data Hub. This is the "brain" of the platform, responsible for cleansing, validating, and transforming the raw data into meaningful and auditable ESG metrics. A core component of this engine is the Greenhouse Gas (GHG) Accounting Module. This module contains a vast, and continuously updated, database of thousands of internationally recognized emission factors. It uses this database to automatically calculate a company's carbon footprint across Scope 1, Scope 2, and the highly complex 15 categories of Scope 3, all in accordance with the GHG Protocol standard. Beyond carbon, this engine can calculate a wide array of other metrics, from water withdrawal rates and waste diversion percentages to employee turnover and injury frequency rates. All of this calculated data, along with the original source data, is stored in a centralized, audit-ready data hub. This creates a "single source of truth" for all of the company's ESG information, ensuring consistency and traceability from the final reported number all the way back to the original utility bill or supplier survey response.
The third critical architectural pillar is the Reporting, Disclosure, and Frameworks Module. This is the primary output of the platform and a key reason for its adoption. The ESG reporting landscape is a complex "alphabet soup" of different standards and regulations, and this module is designed to navigate that complexity. The platform comes pre-loaded with templates and content frameworks for all the major global standards, including the GRI Standards, the SASB Standards for industry-specific disclosures, the TCFD framework for climate risk reporting, and the questionnaires for major rating agencies like CDP and EcoVadis. The software automatically maps the data from the central data hub to the specific requirements of each of these frameworks, allowing a company to efficiently generate multiple different reports from a single, consistent dataset. This dramatically simplifies the reporting process and ensures that the company's disclosures are compliant, consistent, and meet the specific expectations of different stakeholders, from investors to regulators.
Finally, the entire architecture is supported by a robust Governance, Workflow, and Analytics Layer. ESG management is a collaborative, cross-functional process, and this layer provides the tools to manage it effectively. It includes a workflow engine that allows a sustainability manager to assign data collection tasks to specific individuals across the organization, set deadlines, and track their progress. It provides data governance features, such as role-based access controls and approval workflows, to ensure data integrity. The analytics component of this layer provides interactive dashboards and data visualizations that allow managers to track their performance against their ESG targets, identify "hotspots" of risk or inefficiency, and benchmark their performance against industry peers. This layer is what transforms the platform from a simple reporting tool into a true management system, providing the data-driven insights needed to set strategy, manage performance, and drive continuous improvement across the entire organization.
Top Trending Reports: