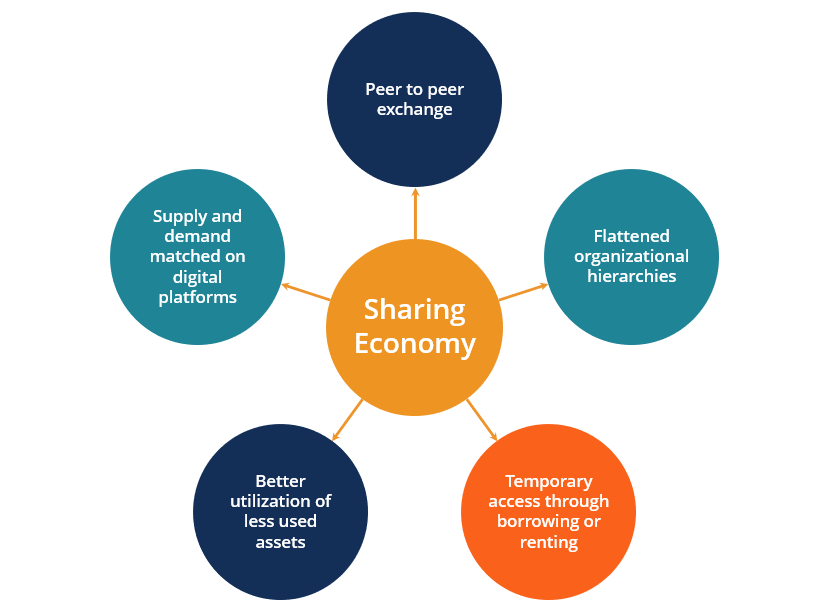
Several structural forces are propelling Sharing Economy Market Growth across transportation, accommodation, logistics, and everyday services. Ubiquitous smartphone adoption and reliable mobile connectivity give consumers instant access to platforms that match supply and demand in real time. Digital payment systems, from cards to mobile wallets, make low‑friction, small‑ticket transactions viable at scale. Urbanization concentrates both assets and users, increasing liquidity for ride‑hailing, micromobility, and short‑term rentals. Meanwhile, economic uncertainty and wage stagnation in many regions drive individuals to monetize spare rooms, vehicles, or skills. Together, these trends create fertile ground for sharing models that promise extra income for providers and cost savings or convenience for users, fueling robust growth in the global Sharing Economy Market.
Consumer preferences are another powerful driver of Sharing Economy Market Growth. Younger generations, in particular, often prioritize access, flexibility, and experiences over ownership of cars, homes, or luxury goods. Subscription services, on‑demand rentals, and pay‑per‑use models align with lifestyles that involve frequent moving, travel, and experimentation. Environmental awareness also encourages reconsideration of underutilized assets: why leave a car parked 95% of the time when it could generate income and reduce the need for new vehicles? Platforms capitalize on these attitudes by marketing sharing as both economical and sustainable. As user familiarity grows, network effects strengthen: more providers attract more users, which attract more providers, creating self‑reinforcing expansion in many verticals.
Technological innovation underpins much of the current Sharing Economy Market Growth. Advanced matching algorithms reduce wait times and improve asset utilization, making services more reliable and attractive. Real‑time pricing adjusts for supply‑demand imbalances, incentivizing providers to participate during peak periods while maximizing revenue. Identity verification, background checks, and reputation systems reduce perceived risk in peer‑to‑peer interactions, broadening the pool of participants willing to transact with strangers. Integration with mapping, navigation, and IoT sensors further enhances operational efficiency: vehicles can be located and unlocked via apps; smart locks manage property access; usage can be metered precisely for fair billing. These technical foundations allow sharing platforms to scale globally while maintaining consistent user experiences.
Public policy and corporate strategies also shape Sharing Economy Market Growth. In some cities, authorities actively partner with platforms to expand mobility options, reduce congestion, or improve tourism capacity, offering pilot programs or regulatory sandboxes. Municipalities experimenting with shared bikes, scooters, or car‑sharing fleets sometimes rely on private platforms as implementation partners. At the corporate level, traditional firms increasingly adopt “platform” or “as‑a‑service” extensions: automakers launch car‑sharing or subscription models; hotel chains explore home‑sharing partnerships; equipment manufacturers create rental marketplaces. This hybridization blurs boundaries between incumbents and disruptors, embedding sharing principles more deeply into mainstream business. As regulations stabilize and business models mature, these combined forces suggest that Sharing Economy Market Growth will remain a significant feature of the global economic landscape.
Explore More Like This in Our Regional Reports:
APAC Marketing Automation Software Market